Is RAID 1 or 5 better?
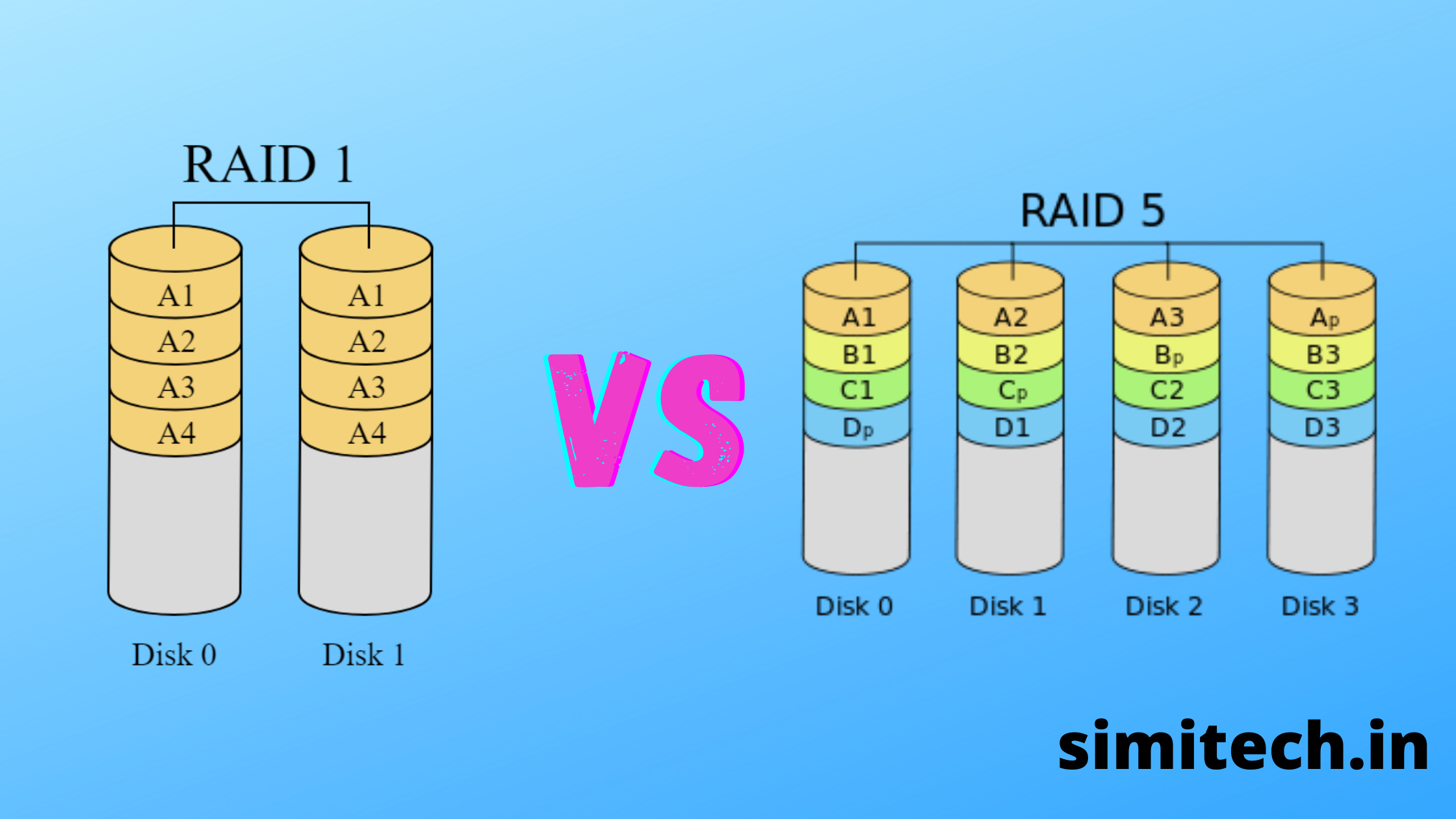
Is RAID 5 better than RAID 1
Raid 5 has good failure resistance and better security. The performance is great in Raid 1, but in Raid 5, performance is slow due to disks' redundancy. Data cannot be accessed from a failed drive in Raid 1, whereas data can be accessed from a failed drive in Raid 5.
Why use RAID 5 instead of RAID 1
In RAID 5, data is equally divided in all disks and minimum number of physical disks needed is 3. The main advantages of RAID 5 over RAID 1 are no need of large space, supports data accessing at the time of recovery and high security of data. RAID 5 is generally suited for medium level of applications.
Why is RAID 5 better
Advantages of RAID 5
Considered a good all-around RAID system, RAID 5 combines the better elements of efficiency and performance among the different RAID configurations. Fast, reliable read speed is a major benefit. This RAID configuration also offers inexpensive data redundancy and fault tolerance.
How much faster is RAID 5 than RAID 1
RAID 1 arrays read/write at the same speed as a single disk, sometimes a little higher due to writing to multiple disks simultaneously. RAID 5 has a slower write speed as time is spent calculating blocks to slice and where to put them along with recording checksum on a separate disk.
Is RAID 1 enough
Unlike RAID 0, RAID 1 provides protection against disk failure. The storage volume will remain accessible even if one of the disks in the mirror set were to fail. However, a mirror cannot withstand the failure of multiple disks unless multiple mirrors are present.
Is RAID 1 a good idea
Combining hard disks in a RAID 1 is always worthwhile when one requires high availability of their stored data. Since the storage of these redundant arrays is relatively expensive, they are not suitable for backing up large amounts of data.
Is RAID 5 slow
RAID 5 arrays have relatively slow write performance because parity information must be written to the disks alongside the actual data. RAID 6 arrays are even slower because they store a greater volume of parity data than RAID 5 arrays do.
Why is RAID 1 better
Unlike RAID 0, RAID 1 provides protection against disk failure. The storage volume will remain accessible even if one of the disks in the mirror set were to fail. However, a mirror cannot withstand the failure of multiple disks unless multiple mirrors are present.
Can RAID 5 fail
When a single disk in a RAID 5 disk array fails, the disk array status changes to Degraded. The disk array remains functional because the data on the failed disk can be rebuilt using parity and data on the remaining disks. If a hot-spare disk is available, the controller can rebuild the data on the disk automatically.
Does RAID 1 reduce performance
RAID 1 offers slower write speeds but could offer the same read performance as RAID 0 if the RAID controller uses multiplexing to read data from disks. Where data reliability is less of a concern and speed is important.
Is RAID 1 good for SSD
RAID 1 systems provide more reliability, where data mirrors a second SSD. In this system, data is stored twice simultaneously by writing on both the data drive and a mirror drive. If a drive fails, it can be recovered from the mirror drive. That said, RAID 1 performs slower and doubles the number of SSDs needed.
Is RAID 1 necessary with SSD
SSD RAID may not be necessary, but the system's performance and speed, data security, and reliability and endurance make it a popular method of ensuring data availability and redundancy.
Why is RAID 1 slow
Writes to a RAID 1 unit is slower compared with RAID 0, but about the same as writing to a single disk. This is because the entire data is written to two disks, but in parallel.
Is RAID 1 fast
RAID 1, on the other hand, offers mirroring, so the same data is available in two disks. RAID 1 is slightly slower than RAID 0 because there are two writes, but the read operations are equally fast. Due to the above differences, these RAID levels work well in different scenarios.
Is RAID 5 bad for SSD
RAID 5 is generally not recommended for SSDs (Solid-State Drives) due to several reasons: Write Amplification: RAID 5 involves striping data across multiple drives and also calculating and storing parity information.
Which RAID is best for SSD
RAID 4. This is the preferred configuration for SSD RAIDs by storing all parity data on a single SSD. This provides the fastest performance with the greatest capacity while still protecting you if an SSD dies.
Is it safe to use RAID 5 on SSD
Moreover, RAID 5 is cost-efficient and has become popular for SSD subsystems. It increases security via parity data and improves speed by interleaving data across storage drives. Upon drive failure, subsequent reads can be calculated from the distributed parity; they will lose no data.
Is raid 5 slow
RAID 5 arrays have relatively slow write performance because parity information must be written to the disks alongside the actual data. RAID 6 arrays are even slower because they store a greater volume of parity data than RAID 5 arrays do.
Does RAID 5 reduce storage
RAID 5 results in the loss of storage capacity equivalent to the capacity of one hard drive from the volume. For example, three 500GB hard drives added together comprise 1500GB (or roughly about 1.5 terabytes) of storage.
Should I use RAID 5 with SSD
Yes, RAID 5 is generally suitable for SSDs. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) 5 provides a balance between performance and data protection. It distributes data across multiple drives, offering redundancy by using parity information.
Can RAID 5 lose 2 drives
If a second disk in a RAID 5 disk array fails, the array also fails and its data is not accessible. If a second disk in a RAID level 5 disk array fails, you must replace the failed disks, then delete and recreate the disk array.
Do I need RAID 1 for SSD
RAID 1 systems provide more reliability, where data mirrors a second SSD. In this system, data is stored twice simultaneously by writing on both the data drive and a mirror drive. If a drive fails, it can be recovered from the mirror drive. That said, RAID 1 performs slower and doubles the number of SSDs needed.
How many drives can fail in RAID 1
two-
Unlike RAID 0, RAID 1 provides data redundancy, creating a fault-tolerant array. So, in a two-disk RAID 1 configuration, if one disk drive fails, the second disk drive contains the same data, ergo, data was not lost and can be easily recovered. As a result, fault tolerance has been achieved.
Is RAID 1 slower than single drive
Lower performance – RAID 1 is designed to provide consistent data across both drives in the array, which means it's slower than a single drive. Increased cost – Due to the need for two drives, RAID 1 is one of the more expensive configurations available.
Is RAID 5 fault tolerant
RAID 5 – strips the disks similar to RAID 0, but doesn't provide the same amount of disk speed. Has fault tolerance without the loss of any data.



0 Comments